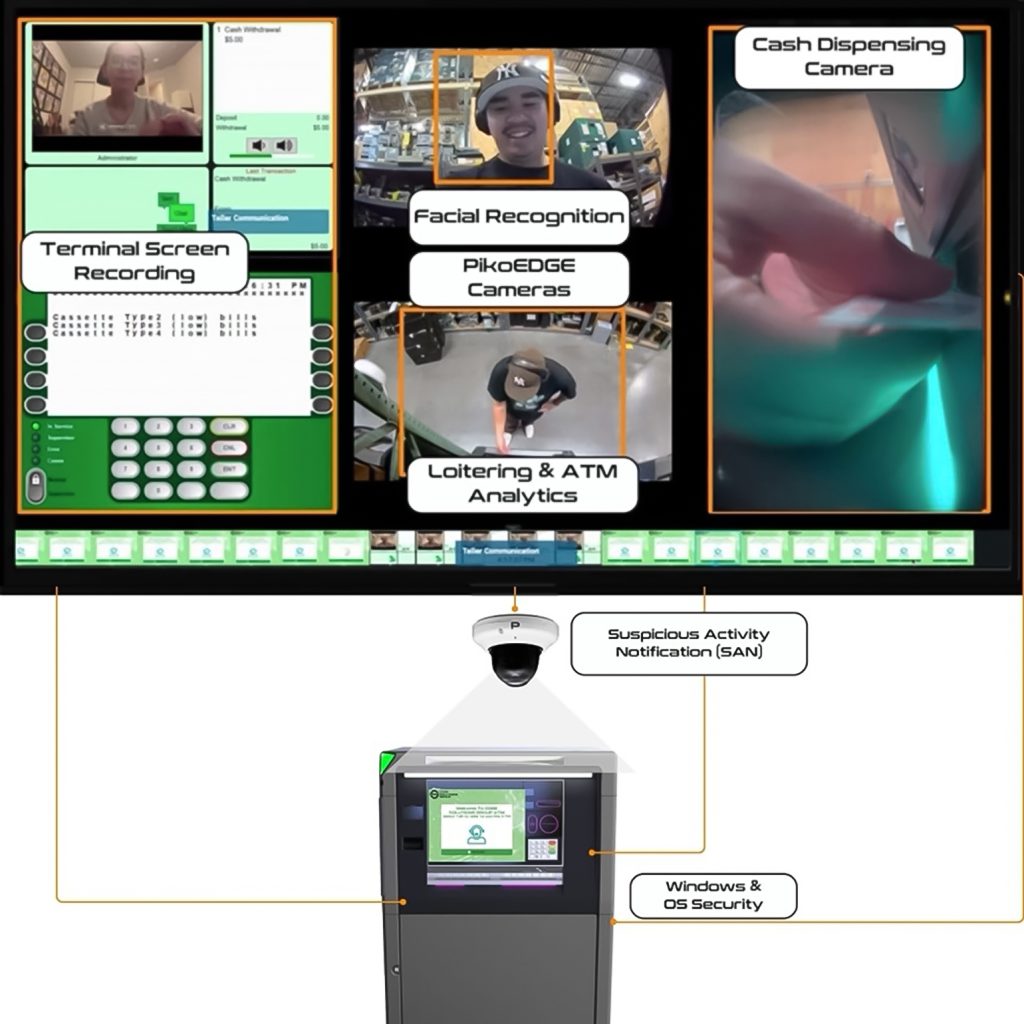
ATM security requires more than just traditional surveillance. A comprehensive strategy involves real-time monitoring, intelligent analytics and proactive threat detection to address a variety of vulnerabilities. The following are some of the common threats and how they can be mitigated through a layered security approach:
- Hook and Chain, Physical Attacks: These involve brute force attempts to physically extract cash from terminals. Reinforced hardware and physical protections help deter these types of attacks.
- Card Skimming and Cash Harvesting: Criminals use devices to illegally capture card data or access cash. Anti-skimming technologies and secure software protocols can reduce this risk.
- Regulation E Claims: In cases of disputed transactions, security systems can support compliance efforts by providing transaction data and video verification.
- Terminal Jackpotting: This involves manipulating terminal software to fraudulently dispense cash. Monitoring for software anomalies and applying security patches regularly helps prevent this.
- External Dispenser Manipulation: Criminals may attempt to tamper with cash dispensing mechanisms. Hardware protections and tamper detection can alert institutions to these risks.
- Software Vulnerabilities: Malware and cyber threats often exploit outdated or unprotected systems. AI-based endpoint security tools can help safeguard ATM operating systems.
- Cash Dispensing and Cash Trapping: Devices placed on ATMs can trap cash during a transaction. Physical sensors and tamper alerts can detect and respond to these threats.
- Data Compliance: Encryption of hard drive data ensures that sensitive information is protected, supporting data integrity and privacy requirements.
- Transaction Reversal Fraud: Criminals may try to reverse transactions after receiving cash. Monitoring transaction patterns can help identify and mitigate this type of fraud.
- Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attacks: Attackers may intercept or alter communications between the ATM and its host. Secure communication channels and encryption help guard against interception and impersonation.
Integrating ATMs, ITMs and point-of-sale systems into the surveillance network — ATM Terminal Security allows for seamless monitoring of transactional operations.
Terminal Security Suite Overview
The Terminal Security suite addresses common security concerns related to ATMs and ITMs by integrating a range of advanced tools:
- PikoVIDEO
- PikoTERMINAL
- PikoVERIFY
- PikoANALYTICS
- RemoteView Electronic Journals and Security Plus
- SAN Camera and Fraudulent Detection Engine
This system combines AI-based surveillance, transaction validation and screen recording to help monitor and respond to both physical and digital threats. Key features include real-time monitoring and automated threat detection, which support terminal security operations and assist in dispute investigations.